Introduction
The Ultraviolet (UV) Index is a crucial tool for assessing the strength of UV radiation from the Sun and understanding the potential risks associated with sun exposure. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to the UV Index, covering its purpose, scale, categories, factors influencing UV intensity, health risks, and protective measures. By understanding the UV Index, you can make informed decisions about sun protection and minimize the harmful effects of UV radiation on your skin and eyes.
The Purpose of the UV Index
The primary purpose of the UV Index is to quantify the intensity of UV radiation at a specific location on the Earth’s surface. UV radiation consists of UVA, UVB, and UVC rays, with UVA being the least harmful and UVC being almost entirely absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere. The UV Index focuses on UVA and UVB, as these are the rays that reach the Earth’s surface. Read More…
By providing a numerical value, the UV Index helps individuals understand the potential harm caused by UV rays and take appropriate sun protection measures. It serves as a public health tool, guiding people in determining the level of risk associated with UV exposure at different times and locations.
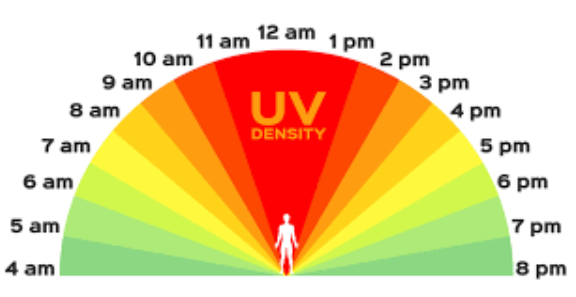
The UV Index Scale and Categories
The UV Index is typically measured on a scale ranging from 0 to 11+, although values above 11 can occur in certain regions with extreme conditions. The index is divided into five categories that represent increasing levels of risk associated with UV exposure:
Low (0-2): Minimal risk. No protection against UV radiation is generally required.
Moderate (3-5): Moderate risk. Some precautions, such as wearing hats and sunglasses, applying sunscreen, and seeking shade, are recommended.
High (6-7): High risk. Protection measures are crucial, including wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen with a high SPF, and minimizing sun exposure during peak hours.
Very High (8-10): Very high risk. Extra precautions are necessary, such as wearing UV-blocking sunglasses, seeking shade, and reapplying sunscreen frequently.
Extreme (11+): Extremely high risk. Take all possible precautions, including staying indoors during peak hours and avoiding direct sun exposure whenever possible.
Factors Influencing UV Intensity
Several factors influence the intensity of UV radiation at a specific location and time:
Season: UV levels tend to be higher during the summer months due to the Sun’s angle and longer daylight hours.
Latitude: UV radiation is more intense near the equator and decreases as you move farther away from it.
Altitude: UV intensity increases with altitude, as the atmosphere becomes thinner and offers less protection.
Cloud cover: Clouds can reduce UV radiation but not completely block it. Even on a cloudy day, significant UV exposure can occur.
Understanding these factors can help you gauge the UV intensity in different conditions and locations, enabling you to adjust your sun protection measures accordingly.
Health Risks of Excessive UV Exposure
Overexposure to UV radiation can have detrimental effects on both short-term and long-term health. Short-term effects include sunburn, which is characterized by red, painful, and inflamed skin. Severe sunburns can lead to blistering and increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
Long-term exposure to UV radiation can cause various long-lasting effects, including premature aging of the skin, wrinkles, age spots, and loss of skin elasticity. Prolonged and unprotected




 1v1 lol unblocked 66 ez
1v1 lol unblocked 66 ez