Managing diabetes can be a challenging task, especially when it comes to monitoring blood glucose levels. But what if you could monitor your glucose levels 24/7 without having to prick your finger multiple times a day? Thanks to advancements in Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) devices, this is now possible! With real-time tracking and alerts, CGMs are revolutionizing diabetes management by providing patients with more accurate data than ever before. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of continuous glucose monitoring, the different types of CGM devices available on the market today, and how to use them effectively. So sit back and get ready to learn about the exciting world of CGMs!
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices (CGM)
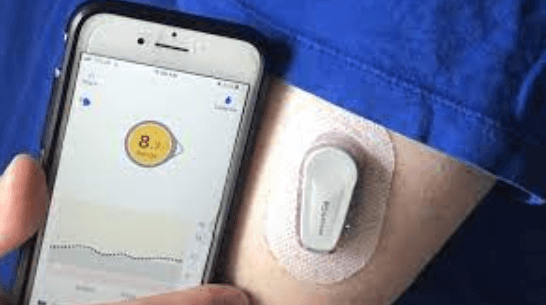
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) devices are wearable sensors that offer real-time tracking of glucose levels in the body. The sensor is attached to the skin and measures glucose levels in interstitial fluid, which is a thin layer of fluid that surrounds cells. CGMs can provide patients with an accurate picture of their glucose trends throughout the day and night, including after meals and during exercise. Read More…
The data collected by CGMs can help patients make informed decisions about insulin dosing, diet, and physical activity. With continuous monitoring, patients can avoid hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia episodes that could have otherwise gone unnoticed until it was too late.
One significant advantage of using CGMs over traditional blood glucose meters is the ability to receive alerts when glucose levels reach predetermined high or low thresholds. This feature provides peace of mind for both patients and caregivers who may be concerned about potential complications from uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
While many people use CGM devices as part of their diabetes management plan, they may not be suitable for everyone. It’s important to speak with your healthcare provider before deciding if a CGM device is right for you. These advancements in technology have revolutionized how we manage diabetes today!
Benefits of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) devices have revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time insight into glucose levels. The benefits of CGMs are numerous and can significantly improve the quality of life for people with diabetes.
One major benefit is that CGMs provide a more comprehensive view of blood sugar trends throughout the day, allowing individuals to make better-informed decisions about their insulin dosages, food choices, and activity levels.
Another advantage is that continuous monitoring reduces the need for frequent finger pricks. Instead, users can simply check their device’s readings to get an accurate picture of their glucose level.
Additionally, CGMs can alert users when their glucose levels are trending outside their target range or if they experience sudden spikes or drops in blood sugar. This feature allows more prompt interventions to prevent dangerous complications such as hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
The convenience factor cannot be overstated. With real-time monitoring via mobile apps or other devices connected to your phone or computer system through Bluetooth technology, managing diabetes becomes less intrusive on daily activities while also offering peace of mind knowing you have access to personalized data at anytime from anywhere in the world.
Types of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices
There are several types of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices that are available in the market today. Each device has its own unique features and functionalities, catering to different user needs.
One type of CGM is the real-time CGM which provides continuous readings every few minutes with alerts for low and high blood sugar levels. This device requires a sensor to be inserted under the skin, connected to a transmitter which sends data wirelessly to a receiver or smartphone.
Another type is the intermittently viewed CGM which allows users to check their glucose levels whenever they want by scanning a sensor worn on their body using a reader or mobile app.
Some devices combine both real-time and intermittently viewed functionality while others offer additional features such as insulin pump integration or predictive analytics for future glucose trends.
It’s important for individuals with diabetes to research and consult with healthcare professionals before choosing a CGM device that best suits their lifestyle.
How to Use a Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device
Using a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) device may seem intimidating at first, but it is actually quite simple. Here are some basic steps on how to use a CGM:
Firstly, choose the area where you want to place the sensor. It can be inserted into your abdomen or upper buttock area. Ensure that the skin is clean and dry before insertion.
Next, insert the sensor by following manufacturer instructions carefully. This usually involves removing a protective cover from the adhesive patch and attaching it firmly onto your skin.
Once attached, turn on the CGM device and wait for it to start reading your glucose levels in real-time. You can check readings anytime by looking at the screen of your device.
It’s important to calibrate your CGM device regularly according to manufacturer’s instructions as this ensures accurate readings over time.
Remember that while using a CGM can provide you with valuable information about your glucose levels throughout day and night, it should not replace regular fingerstick checks or medical advice from healthcare professionals.
With these simple steps, using a continuous glucose monitoring device becomes an easy part of diabetes management routine!



 Transforming Your Smart Home: Exploring Google Home Compatible Devices for Seamless Integration and Enhanced Automation
Transforming Your Smart Home: Exploring Google Home Compatible Devices for Seamless Integration and Enhanced Automation